
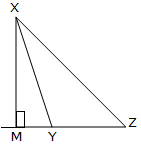
New!!: Altitude (triangle) and Central line (geometry)

In geometry central lines are certain special straight lines associated with a plane triangle and lying in the plane of the triangle.
In a right triangle, a cathetus (originally from the Greek word Κάθετος plural: catheti), commonly known as a leg, is either of the sides that are adjacent to the right angle. New!!: Altitude (triangle) and Base (geometry) In geometry, a base is a side of a polygon or a face of a polyhedron, particularly one oriented perpendicular to the direction in which height is measured, or on what is considered to be the "bottom" of the figure. New!!: Altitude (triangle) and Barycentric coordinate system In geometry, the barycentric coordinate system is a coordinate system in which the location of a point of a simplex (a triangle, tetrahedron, etc.) is specified as the center of mass, or barycenter, of usually unequal masses placed at its vertices.
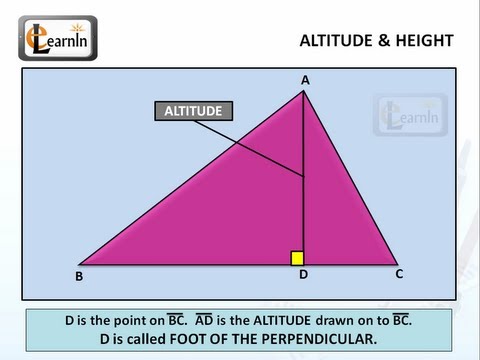
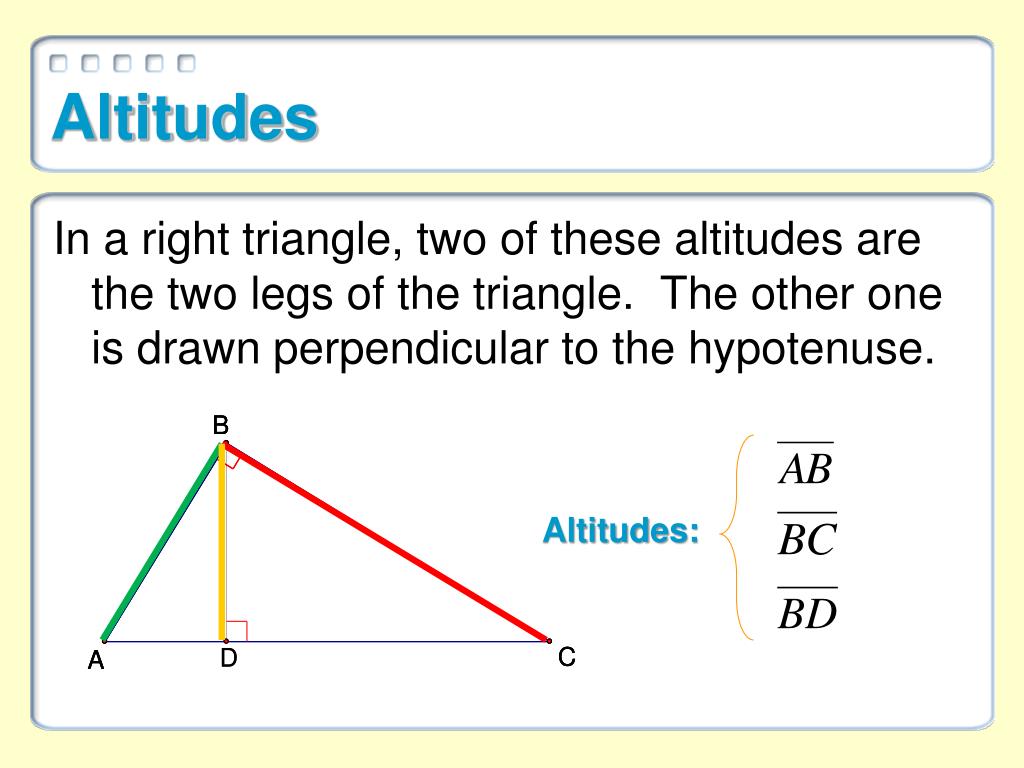
, Latin letters used in mathematics, Line segment, List of geometry topics, List of Greek and Latin roots in English/C, List of interactive geometry software, List of numbers, List of theorems, List of triangle inequalities, List of triangle topics, Medial triangle, Median (geometry), Midpoint, Midpoint polygon, Musselman's theorem, Nine-point center, Nine-point circle, Nine-point conic, Nine-point hyperbola, Olry Terquem, Orthocentric system, Orthocentroidal circle, Orthodiagonal quadrilateral, Pedal triangle, Perpendicular, Polar circle (geometry), Pythagorean theorem, Quadrilateral, Right triangle, Similarity (geometry), Simson line, Solution of triangles, Tangential quadrilateral, Tangential triangle, There is No Natural Religion, Triangle, Triangle center, Triangular prism, Trigonometry of a tetrahedron, Trilinear coordinates, Trilinear polarity, Van Lamoen circle, Viviani's theorem. ĩ2 relations: Acacia (fraternity), Acute and obtuse triangles, Altitude (disambiguation), Angle bisector theorem, Area, Barycentric coordinate system, Base (geometry), Cathetus, Central line (geometry), Centre (geometry), Centroid, Cevian, Circumconic and inconic, Circumscribed circle, Collinearity, Compass-and-straightedge construction, Complete quadrangle, Concurrent lines, Conway triangle notation, Cubic plane curve, Cyclic quadrilateral, De Longchamps point, Dissection into orthoschemes, Droz-Farny line theorem, Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers, Equilateral triangle, Equivariant map, Euler line, Exeter point, Extended side, Fagnano's problem, Fuhrmann circle, Geometric mean theorem, Giovanni Fagnano, Harmonic mean, Height, Height (disambiguation), Heptagonal triangle, Heron's formula, Heronian triangle, Hilbert space, Holditch's theorem, Hyperbolic sector, Incenter, Incircle and excircles of a triangle, Integer triangle, Isogonal conjugate, Isosceles triangle, Johnson circles, Kenneth Wayne Bushnell. In geometry, an altitude of a triangle is a line segment through a vertex and perpendicular to (i.e., forming a right angle with) a line containing the base (the side opposite the vertex).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
